Preparatory Course for ACCA Qualification Examination
Overview
The preparatory course is ideal for working adults who are new to finance or aiming to switch to finance or those who are already working in finance and seeking a formal accountancy qualification for career progression. It equips learners (students) with the business skillset on how financial information is recorded and interpreted to address business challenges and ready to sit for the modular ACCA examination to attain the ACCA accountancy qualification.
The ACCA Qualification, awarded by the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants requires learners (students) to take a number of modular exams and to complete an online ACCA's ethics and professional skills module, plus three (3) years' practical experience to be awarded the ACCA Qualification.
- Modules
1 . Business and Technology (BT/FBT)
The syllabus introduces students who may not have a business background, to the business, which as an entity is made up of people and systems which interact with the environment and with each other.
The syllabus begins with examining the purpose and types of business which exist, the key stakeholders and the rights and responsibilities that businesses have in connection with them, exploring the external influences that affect the business in its environment, including economic, legal, social and technological factors.
The syllabus then examines the structure and functions of business, focusing on corporate governance and the specific accounting related roles in this process, particularly in financial reporting, assurance, control and compliance. The syllabus also covers financial systems including the impact of financial technology. The syllabus then introduces key leadership, management and people issues such as effective individual and team behaviour, motivation and personal effectiveness.
The final section of the syllabus examines how behaviour at all levels within business should be underpinned by accepted professional ethics and professional values.
2 . Management Accounting (MA/FMA)
The syllabus introduces candidates to elements of management accounting which are used to make and support decisions.
The syllabus starts by introducing the nature, the source and purpose of management information followed by the statistical techniques used to analyse data. Then the syllabus addresses cost accounting and the costing techniques used in business which are essential for any management accountant.
The syllabus then looks at the preparation and use of budgeting and standard costing and variance analysis as essential tools for planning and controlling business activities. The syllabus concludes with an introduction to measuring and monitoring the performance of an organisation.
3 . Financial Accounting (FA/FFA)
The syllabus introduces the candidate to the fundamentals of the regulatory framework relating to accounts preparation and to the qualitative characteristics of useful information.
The syllabus then covers drafting financial statements and the principles of accounts preparation. The syllabus then concentrates in depth on recording, processing, and reporting business transactions and events. The syllabus then covers the use of the trial balance and how to identify and correct errors, and then the preparation of financial statements for incorporated and unincorporated entities.
The syllabus then moves in two directions, firstly requiring candidates to be able to conduct a basic interpretation of financial statements; and secondly requiring the preparation of simple consolidated financial statements from the individual financial statements of group incorporated entities.
4 . Corporate and Business Law (LW)
This syllabus is divided into eight areas. The syllabus starts with an introduction to the overall English legal system such as the court system and sources of law. It then leads into the area of the law of obligations including contract and tort, which underpin business transactions generally.
The syllabus then covers a range of specific legal areas relating to various aspects of business of most concern to finance professionals. These are the law relating to employment and the law relating to companies. These laws include the formation and constitution of companies, the financing of companies and types of capital, and the day-to-day management, the administration and regulation of companies and legal aspects of insolvency law.
The final section links back to all the previous areas. This section deals with corporate fraudulent and criminal behaviour.
5 . Performance Management (PM)
This syllabus builds on the knowledge gained in Management Accounting (MA) and seeks to examine candidates' understanding of how to manage the performance of a business. It also prepares candidates for more specialist capabilities which are covered in Advanced Performance Management (APM).
The syllabus begins by focusing on the information needs, technologies and systems required by organisations to manage and measure performance in the modern, competitive environment. It is vital for an accountant to understand how information systems and developments in technology influence the management accounting techniques employed and how vital information systems are in the mechanisms of managing and controlling an organisation.
The syllabus then introduces more specialised costing and management accounting topics. There is some knowledge assumed from Management Accounting (MA) - primarily overhead treatments. The objective here is to ensure candidates have a broader background in management accounting techniques. The syllabus then considers decision-making. Candidates need to appreciate the problems surrounding scarce resources, pricing and make-or-buy decisions, and how this relates to the assessment of performance. Risk and uncertainty are a factor of real-life decisions and candidates need to understand risk and be able to apply some basic methods to help resolve the risks inherent in decision-making.
Budgeting is an important aspect of many accountants' lives. The syllabus explores different budgeting techniques, including quantitative techniques, and the problems inherent in them. The behavioural aspects of budgeting are important for accountants to understand, and the syllabus includes consideration of the way individuals react to a budget. The preparation of fixed, flexible and incremental budgets is assumed knowledge from Management Accounting (MA).
Standard costing and variances are then built on. All the variances examined in Management Accounting (MA) are assumed knowledge in Performance Management (PM). Mix and yield variances and planning and operational variances are explored here, and the link is made to performance management. It is important for accountants to be able to interpret the numbers that they calculate and discuss what they mean in the context of performance.
The syllabus concludes with performance measurement and control. This is a major area of the syllabus. Accountants should appreciate the importance of both financial and non-financial performance measures in management and should also appreciate the difficulties in assessing performance in divisionalised businesses and the problems caused by failing to consider external influences on performance. This section leads directly to Advanced Performance Management (APM).
All of the subject areas covered in this syllabus could be examined in either a public sector or private sector context.
The final topic under Employability and Technology Skills contains outcomes relating to the demonstration of appropriate digital and employability skills in preparing for and taking the PM examination. This includes being able to interact with different question item types, manage information presented in digital format and being able to use the relevant functionality and technology to prepare and present response options in a professional manner. These skills are specifically developed by practicing and preparing for the PM examination, using the learning support content for computer-based examinations available via the practice platform and the ACCA website and will need to be demonstrated during the live examination.
6 . Taxation - Singapore (TX-SGP)
This syllabus introduces candidates to the subject of taxation and provides the core knowledge of the underlying principles and major technical areas of taxation, as they affect the activities of individuals and businesses.
In this syllabus, candidates are introduced to the rationale behind and the functions of the tax system. The syllabus then considers the separate taxes that an accountant would need to have a detailed knowledge of, such as income tax from self-employment, employment and investments; the corporation tax liability of individual companies and groups of companies; and the goods and services tax liability of businesses.
Having covered the core areas of the basic taxes, the candidate should be able to compute tax liabilities, explain the basis of their calculations, apply tax planning techniques for individuals and companies and identify the compliance issues for each major tax through a variety of business and personal scenarios and situations.
The final topic under Employability and Technology Skills contains outcomes relating to the demonstration of appropriate digital and employability skills in preparing for and taking the examination. This includes being able to interact with different question item types, manage information presented in digital format and being able to use the relevant functionality and technology to prepare and present response options in a professional manner. These skills are specifically developed by practicing and preparing for the exam, using the learning support content for computer-based exams available via the practice platform and the ACCA website and will need to be demonstrated during the live exam.
7. Financial Reporting (FR)
This syllabus assumes knowledge acquired in Financial Accounting (FA), and develops and applies this further and in greater depth.
The syllabus begins with the Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting with reference to the qualitative characteristics of useful information and the fundamental bases of accounting introduced in the Financial Accounting (FA) syllabus within the Knowledge module.
It then moves into a detailed examination of the regulatory framework of accounting and how this informs the standard setting process. The main areas of the syllabus cover the reporting of financial information for single companies and for groups in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and relevant IFRS Standards. The syllabus also covers the analysis and interpretation of information from financial statements.
Finally, the syllabus contains outcomes relating to the demonstration of appropriate digital and employability skills in preparing for and taking the FR examination. This includes being able to interact with different question item types, manage information presented in digital format and being able to use the relevant functionality and technology to prepare and present response options in a professional manner. These skills are specifically developed by practicing and preparing for the FR exam, using the learning support content for computer-based exams available via the practice platform and the ACCA website and will need to be demonstrated during the live exam.
8 . Audit and Assurance (AA)
This syllabus is essentially divided into six areas. The syllabus starts with the nature, purpose and scope of assurance engagements, including the statutory audit, its regulatory environment, and introduces governance and professional ethics relating to audit and assurance. It then leads into planning the audit and performing risk assessment.
The syllabus then covers a range of areas relating to an audit of financial statements including the scope of internal control and the role and function of internal audit. These include, evaluating internal controls, audit evidence, and a review of the financial statements. In addition to final review procedures, the syllabus concentrates on reporting, including the form and content of the independent auditor's report.
Finally, the syllabus contains outcomes relating to the demonstration of appropriate digital and employability skills in preparing for and taking the AA examination. This includes being able to interact with different question item types, manage information presented in digital format and being able to use the relevant functionality and technology to prepare and present response options in a professional manner. These skills are specifically developed by practicing and preparing for the AA exam, using the learning support content for computer-based exams available via the practice platform and the ACCA website and will need to be demonstrated during the live exam.
9 . Financial Management (FM)
This syllabus is designed to equip candidates with the skills that would be expected from a finance manager responsible for the finance function of a business. It prepares candidates for more advanced and specialist study in Advanced Financial Management.
The syllabus, therefore, starts by introducing the role and purpose of the financial management function within a business. Before looking at the three key financial management decisions of investing, financing, and dividend policy, the syllabus explores the economic environment in which such decisions are made.
The next section of the syllabus is the introduction of investing decisions. This is done in two stages - investment in (and the management of) working capital and the appraisal of long-term investments.
The next area introduced is financing decisions. This section of the syllabus starts by examining the various sources of business finance, including dividend policy and how much finance can be raised from within the business. It also looks at the cost of capital and other factors that influence the choice of the type of capital a business will raise. The principles underlying the valuation of business and financial assets, including the impact of cost of capital on the value of business, is covered next. The syllabus then covers an introduction to, and examination of, risk and the main techniques employed in managing such risk.
Section H of the syllabus contains outcomes relating to the demonstration of appropriate digital and employability skills in preparing for and taking the FM examination. This includes being able to interact with different question item types, manage information presented in digital format and being able to use the relevant functionality and technology to prepare and present response options in a professional manner. These skills are specifically developed by practicing and preparing for the FM exam, using the learning support content for computer-based exams available via the practice platform and the ACCA website and will need to be demonstrated during the live exam.
10 . Strategic Business Reporting (SBR-INT)
This syllabus assumes knowledge acquired at the Applied Skills level including the core technical capabilities to prepare and analyse financial reports for single and combined entities.
The syllabus requires students to examine corporate reporting from a number of perspectives, not only from the point of view of the preparer of corporate reports, but also from the perspective of a variety of different stakeholders such as finance providers and investors. The syllabus further requires the assessment and evaluation of the reporting decisions made by management and their implications for a range of stakeholders and entities. It also explores the professional and ethical responsibilities of the accountant to these stakeholders.
The subject matter of the syllabus requires students to have a cohesive understanding of the IASB's Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting® and to use the Framework as a basis for judgement in applying International Financial Reporting Standards in corporate reports. The syllabus considers both the principles and practices of IFRS® Standards and uses these principles as a basis for the preparation of the financial statements of single entities and groups.
The syllabus requires students to reflect on the usefulness of corporate reports to stakeholders including developments in narrative reporting such as Integrated Reporting and sustainability reporting and to discuss the nature of the information that would help stakeholders assess the future prospects of the entity. This involves the analysis and interpretation of corporate reports, and the provision of advice on the reporting implications of transactions.
The penultimate section of the syllabus addresses current developments in corporate reporting and the implications of any potential changes. This includes a discussion of the deficiencies of existing accounting standards and the ability to explain the implications for a business and its stakeholders of significant changes to reporting frameworks. Question scenarios will be based in contemporary business settings, however, candidates will not be required to have detailed knowledge of these businesses. Question scenarios will be current and relevant for example the impact of climate change.
The final section of the syllabus contains outcomes relating to the demonstration of appropriate digital and employability skills in preparing for and taking the SBR examination. This includes being able to access and open exhibits, requirements and response options from different sources and being able to use the relevant functionality and technology to prepare and present response options in a professional manner. These skills are specifically developed by practicing and preparing for the SBR exam, using the learning support content for computer-based exams available via the practice platform and the ACCA website and will need to be demonstrated during the live exam.
11 . Strategic Business Leader (SBL)
This syllabus acts as the key leadership syllabus at the Strategic Professional level and is a substantial integrated examination. The examination requires candidates to demonstrate a range of professional skills demanded by effective leaders or in advising or supporting senior management in directing organisations. The syllabus therefore combines the main functions of organisations in the context of leadership capability. The main capabilities of the Strategic Business Leader syllabus assume essential technical skills and knowledge have been acquired in the Applied Knowledge and Applied Skills examinations where some of the core capabilities of Strategic Business Leader will have been introduced in a subject-specific context, such as governance, internal audit, control, risk, finance, and management. The examination also draws upon a range of ethical and professional skills acquired in the Ethics and Professional Skills module, which should be completed before attempting any of the Strategic Professional examinations.
The Strategic Business Leader syllabus is covered in nine main sections with leadership, professionalism and ethics and corporate governance used as the initial focus for the rest of the syllabus. Excellent leadership involves having a team of capable and responsible directors, setting an appropriate `tone from the top' and embedding appropriate corporate and cultural values within the organisation. This is supported by a sound governance structure and effective management structures. The syllabus begins by examining leadership and having in place responsible and ethical leaders, having an awareness of who they are responsible to This section also covers personal and professional ethics, ethical frameworks - and professional values - as applied to a senior manager or adviser's role and as a guide to appropriate behaviour and conduct in a variety of situations. Clearly linked to organisational leadership is the existence of an effective governance structure within organisations in the broad context of the agency relationship. This aspect of the syllabus focuses on the respective roles and responsibilities of directors, the relevant committee structures and the effective scrutiny of the performance of senior management, demonstrating their accountability by reporting more widely and holistically to stakeholders under an integrated reporting
framework. It is only after the fundamental organisational leadership and governance structures and values are in place that strategy can be determined, and the strategic position of the organisation can be assessed and strategic options evaluated and implemented.
Evaluating strategic options, making strategic choices and implementing strategy requires the organisation's leaders, or their advisers, to fully understand the risks involved so the syllabus then examines the identification, assessment, and control of risk as a key aspect of responsible leadership and management. The syllabus also includes a section relating to and applying IT and security controls at all levels of the organisation from strategic considerations including big data, machine learning, e-business, cloud computing and smart technology through to using IT in the management of information, controlling organisations, and in financial and organisational operations. This section also focuses on the growing importance of `cyber security'
To support the management of risk the syllabus also addresses organisational control in its wider context, including internal audit, review, internal control, and appropriate reporting to implement and support effective governance, including compliance issues related to the safeguard of assets including data security, and decision-support functions.
The syllabus includes financial aspects of managing an organisation, including evaluating available sources of finance and key financial and management accounting techniques to analyse performance and to support decision-making. Candidates need to be aware of legal issues and of the financial reporting and taxation implications of strategic and investment decisions.
The syllabus finally focuses on innovation, performance excellence and change management to enable organisational success and to implement change through effective organisational processes, IT solutions and project management, including the role of new and disruptive technologies in transforming the nature of business analysis and transactions.
The professional skills section of the syllabus links to all others and provides a range of professional skills that the candidate must demonstrate in the exam which will make them more employable, or if already in work, will enhance their opportunities for advancement.
The last section which closely links to the professional skills section is the demonstration of appropriate digital and employability skills in preparing for and taking the SBL examination. This includes being able to use computer functionality and technology to access information and present responses in a professional manner during live examinations.
12 . Advanced Financial Management (AFM)
The syllabus starts by exploring the role and responsibility of a senior executive or advisor in meeting competing needs of stakeholders within the business environment of multinationals. The syllabus then re-examines investment and financing decisions, with the emphasis moving towards the strategic consequences of making such decisions in a domestic, as well as international, context. Candidates are then expected to develop further advisory skills in planning strategic acquisitions and mergers and corporate re-organisations.
The next part of the syllabus re-examines, in the broadest sense, the existence of risks in business and the sophisticated strategies which are employed in order to manage such risks. It builds on what candidates would have covered in the Financial Management syllabus.
The professional skills section of the syllabus links to all others and provides a range of professional skills which the candidate must demonstrate in the exam. These professional skills will make candidates more employable, or if already in work, will enhance their opportunities for advancement.
Section G of the syllabus contains outcomes relating to the demonstration of appropriate digital and employability skills in preparing for and taking the AFM examination. This includes being able to access and open exhibits, requirements and response options from different sources and being able to use the relevant functionality and technology to prepare and present response options in a professional manner. These skills are specifically developed by practicing and preparing for the AFM exam, using the learning support content for computer-based exams available via the practice platform and the ACCA website and will need to be demonstrated during the live exam.
13 . Advanced Performance Management (APM)
This syllabus further develops key aspects introduced in Performance Management at the Applied Skills level.
The syllabus introduces candidates to the strategic role of management accounting as a discipline for planning and controlling performance so that strategic objectives can be set, monitored and controlled. It recognises the impact of external factors on strategic management issues and covers the risks these factors present and how they can be measured and managed. From appreciating the strategic context of performance management and the impact of wider factors, the syllabus examines the issues relating to performance management information systems and their design. It also addresses the impact which developments in technology will have on the performance management and measurement systems used by organisations.
The syllabus then moves from performance management systems to the scope and application of high-level performance measurement techniques in a variety of contexts, including not-for-profit organisations and multi-national businesses. Having covered the strategic aspects of performance management and operational systems for the measurement and control of performance in a wide range of organisational contexts, candidates are then expected to synthesise this knowledge in the role of an advisor to senior management or independent clients on how to assess and control the performance of an entity.
The professional skills section of the syllabus links to all others and provides a range of professional skills which the candidate must demonstrate in the exam. These professional skills will make candidates more employable, or if already in work, will enhance their opportunities for advancement.
The syllabus concludes with outcomes relating to the demonstration of appropriate digital and employability skills in preparing for and taking the APM examination. This includes being able to access and open exhibits, requirements and response options from different sources and being able to use the relevant functionality and technology to prepare and present response options in a professional manner. These skills are specifically developed by practising and preparing for the APM exam, using the learning support content for computer-based exams available via the practice platform and the ACCA website, and will need to be demonstrated during the live exam.
14 . Advanced Taxation - Singapore (ATX-SGP)
This syllabus further develops the key aspects of taxation introduced in the compulsory Taxation syllabus within the Applied Skills module and extends the candidates' knowledge of the tax system, together with their ability to apply that knowledge to the issues commonly encountered by individuals and businesses; such that successful candidates should have the ability to interpret and analyse the information provided and communicate the outcomes in a manner appropriate to the intended audience.
The syllabus builds on the basic knowledge of core taxes from the earlier taxation paper and introduces candidates to tax incentives and stamp duty. As this is an optional paper, aimed at those requiring/desiring more than basic tax knowledge for their future professional lives, the syllabus also extends the knowledge of income tax and corporation tax to encompass further overseas aspects of taxation, the taxation of trusts and additional exemptions and reliefs.
Candidates are not expected to concentrate on the computational aspects of taxation. Instead, this paper seeks to develop candidates' skills of analysis, interpretation and communication. Candidates are expected to be able to use established tax planning methods and consider current issues in taxation.
Section E of the syllabus contains outcomes relating to the demonstration of appropriate digital and employability skills in preparing for and taking the examination. This includes being able to access and open exhibits, requirements and response options from different sources and being able to use the relevant functionality and technology to prepare and present response options in a professional manner. These skills are specifically developed by practicing and preparing for the exam, using the learning support content for computer-based exams available via the practice platform and the ACCA website and will need to be demonstrated during the live exam.
15 . Advanced Audit and Assurance (AAA-INT)
This syllabus further develops key skills introduced in Audit and Assurance at the Applied Skills level.
The syllabus starts with the legal and regulatory environment including money laundering, and professional and ethical considerations, including the Code of Ethics and professional liability. This then leads into procedures in quality management, including quality management relevant at the firm and the engagement level and the acceptance and retention of professional engagements.
The syllabus then covers the audit of financial statements, including planning, and evidence gathering. It then covers the completion, evidence evaluation and review and reporting on an audit of historical financial information. The next section moves onto other assignments including prospective financial information, due diligence and forensic audit as well as the reporting of these assignments.
The next section covers current issues and developments relating to the provision of audit related and assurance services.
The professional skills section of the syllabus links to all others and provides a range of professional skills which the candidate must demonstrate in the exam. These professional skills will make candidates more employable, or if already in work, will enhance their opportunities for advancement.
The final section of the syllabus contains outcomes relating to the demonstration of appropriate digital and employability skills in preparing for and taking the AAA examination. This includes being able to access and open exhibits, requirements and response options from different sources and being able to use the relevant functionality and technology to prepare and present response options in a professional manner. These skills are specifically developed by practicing and preparing for the AAA exam, using the learning support content for computer-based exams available via the practice platform and the ACCA website and will need to be demonstrated during the live exam.
This module is UTAP Claimable for NTUC members.
Please click here for more information.
Who Should Attend ?
Company-funded employees who are required to upskill to support the work functions at the workplace.
Individual who is seeking a course to upskills for a career progression or employability.
School graduates looking to become a finance professional.
Entry Requirement
Minimum Age Requirement :
18
Language Proficiency :
A pass grade at C6 in GCE "O" Level or its equivalent, or
Exceptions : Learners (Students), who have other qualifications, will be assessed on a case-by-case basis.
1 Year Part Complete Diploma from a Polytechnic, or
2 passes at Singapore / Cambridge GCE A Level (grades A- E)
Minimum Academic Requirement :
PLUS3 Singapore / Cambridge GCE O Level passes (grades 1-6 / A1-C6) (in five separate subjects including Mathematics & English), or its equivalent approved by ACCA.
Intake :
Monthly
Fees payable to ASCENSUS INSTITUTE :
- Registration Fee : S$218 w/GST (S$200 w/o GST)
| Level | Module | w/o GST | w/GST |
|---|---|---|---|
| Applied Knowledge (Modules of the ACCA Diploma in Accounting and Business (RQF Level 4)) |
Business and Technology (BT/FBT) | S$ 795.00 | S$ 866.55 |
| Management Accounting (MA/FMA) | S$ 795.00 | S$ 866.55 | |
| Financial Accounting (FA/FFA) | S$ 795.00 | S$ 866.55 | |
| Total Tuition Fee | S$2,385.00 | S$2,599.65 | |
| Applied Skills (Modules of the ACCA Advanced Diploma in Accounting and Business) |
Corporate and Business Law (LW) | S$1,460.00 | S$1,591.40 |
| Performance Management (PM) | S$1,460.00 | S$1,591.40 | |
| Taxation - Singapore (TX-SGP) | S$1,460.00 | S$1,591.40 | |
| Financial Reporting (FR) | S$1,460.00 | S$1,591.40 | |
| Audit and Assurance (AA) | S$1,460.00 | S$1,591.40 | |
| Financial Management (FM) | S$1,460.00 | S$1,591.40 | |
| Total Tuition Fee | S$8,760.00 | S$9,548.40 | |
| Strategic Professional : To Complete 2 Essentials Modules And any 2 of the Optional Modules |
Essentials Module | ||
| Strategic Business Reporting (SBR-INT) | S$1,245.00 | S$1,357.05 | |
| Strategic Business Leader (SBL) | S$1,875.00 | S$2,043.75 | |
| Optional Module | |||
| Advanced Financial Management (AFM) | S$1,095.00 | S$1,193.55 | |
| Advanced Performance Management (APM) | S$1,095.00 | S$1,193.55 | |
| Advanced Taxation - Singapore (ATX-SGP) | S$1,095.00 | S$1,193.55 | |
| Advanced Audit and Assurance (AAA-INT) | S$1,095.00 | S$1,193.55 | |
| Total Tuition Fee for 2 x Essentials and 2 Optional Modules |
S$5,310.00 | S$5,787.90 | |
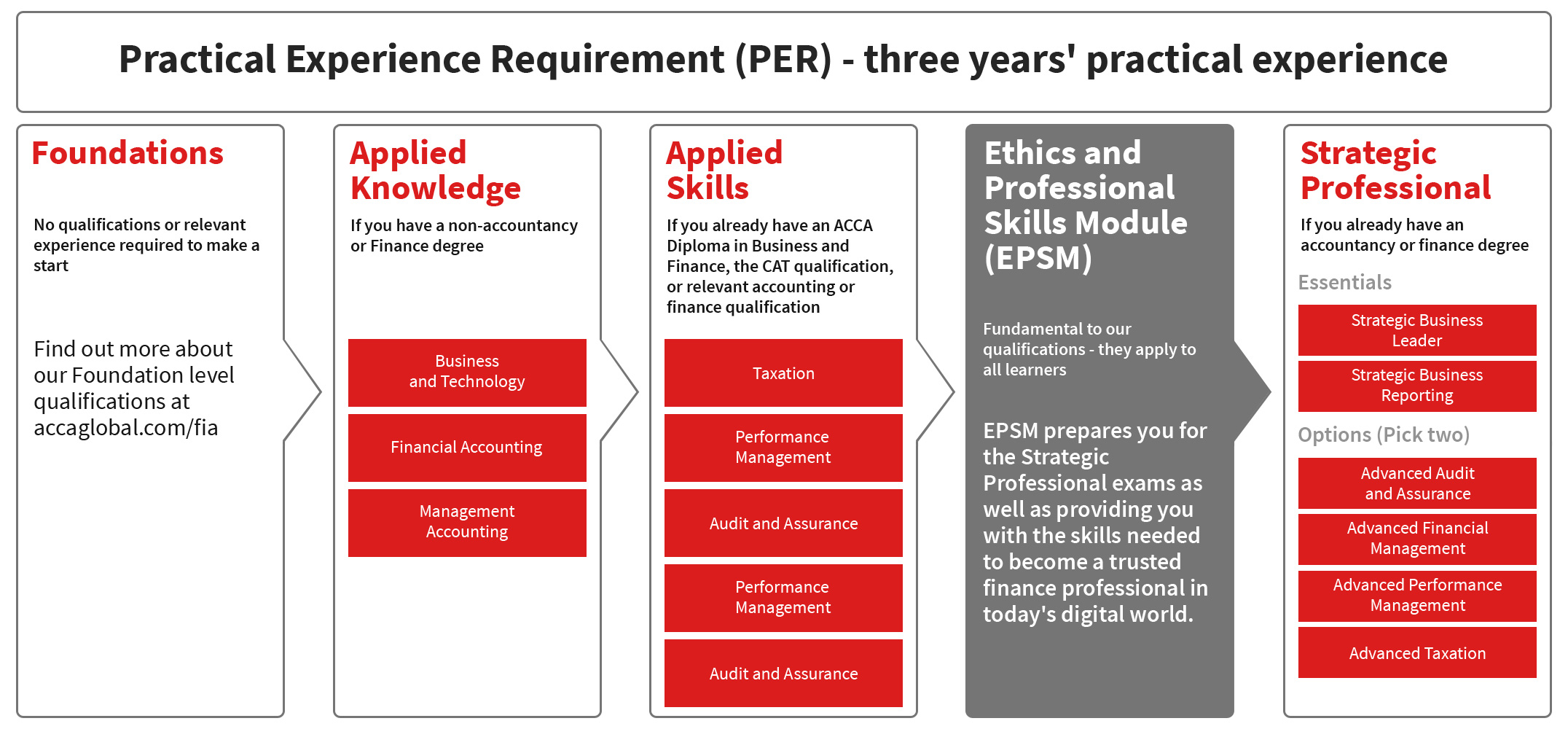
Source : ACCA
Fees payable to ACCA
- Member registration fee : GBP 89
- Annual Fee : GBP 122 per year
- Examination Fee GBP 84 per Module
Graduation Requirement
Association of Chartered Certified Accountants (ACCA) awards will be conferred upon successful completion of the course that obtained a pass in all the required modules and three years' practical experience.



